Detection Of Specific Antigen By Using Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA) Technique
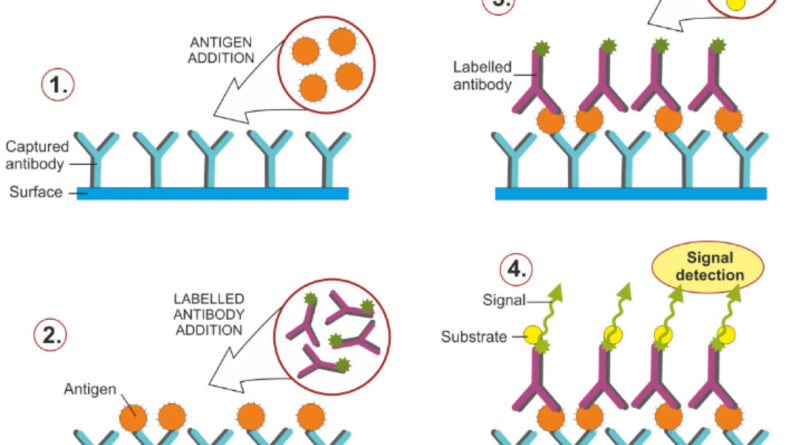
The ELISA is an immunological technique which is used to measure either antigen or antibodies present in serum. For the measurement of the antigens, the ELISA of antibody-coated wells is used and vice versa. In the former case, the test serum containing antigens is used in wells that combines with the specific antibodies immobilised on wells which are detected after adding the second labelled enzyme and substrate.
Requirements
- The test sample (serum sample stored at -75ºC)
- Enzyme conjugate (antibody according to specific antigen is conjugated to enzyme. Horse radish
- peroxidase is the commonly used enzyme. The commonly used cross-linking agents are the
- glutaraldehyde and dimaleimide)
- Substrate (orthophenyldiamine (OPD) or 5-amino salicylic acid)
- Antibody microtest plate (96 well containing plates)
- Diluent (phosphate buffer saline (PBS*); 0.1 M, pH 7.2 or carbonate buffer pH 9.5 or normal saline with 0.1% sodium azide)
- (for preparation of PBS, take 18 ml of Na2HPO4 (14.32 g/200 ml) solution and add to it 7 ml of K2HPO4 (5.44 g/200 ml). Now add 4.38 g of NaCl and make the volume up to 500 ml)
Procedure
- Dilute the antibody to 1:500 in PBS at pH 7.2 and add 75 mm to the bottom of each well.
- Incubate the plates at 4ºC in a moist chamber overnight for 18-20 hours.
- Wash the plates three times with PBS supplemented with 0.05% Tween 20 (PBS-T) for 5 minutes each.
- Add 200 ml of 1% bovine serum albumin in each well and incubate the plates overnight at 4ºC in a moist chamber.
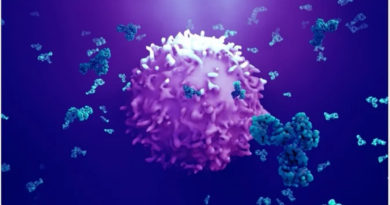
- Add 25 ml of each test sample into the test plates coated with antibody.
- Incubate the plates for 2 hours at room temperature.
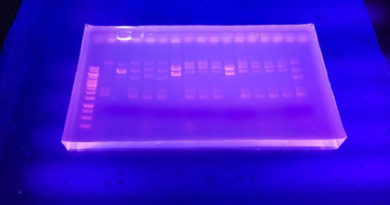
- Wash three times with PBS-T and add 50 ml of peroxidase conjugated antibody to each well.
- Again incubate the plates at room temperature for 2 hours followed by five times washing with PBS-T.
- Now, add 100 ml of freshly prepared substrate i.e. OPD in citrate buffer pH 5.0 and hydrogen peroxide.
- After 30 minutes of incubation at room temperature in a dark box, add 75 ml of 2M H2
- SO4 to stop the reaction.
- Add 75 ml of PBS to make final volume of reaction mixture as 250 ml.
Results
Production of yellow colour as a result of product of enzyme reaction shows a positive result. This is observed with naked eyes against a white background or by measuring the optical density at 492 nm by using a micro ELISA reader by using the following formula:
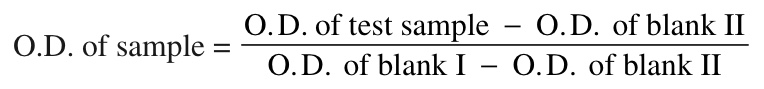
A sample is labelled positive (i) if the yellow colour is stronger than that of negative control, and (ii) if the optical density measured as the ratio of test to negative control is more than 2:1.
O.D. of blank I = It is average optical density of 5-7 negative controls
O.D. of blank II = It is the optical density of 100 ml substrate, 75 ml of 75M H2SO4 and 75 ml of PBS
Reference:
Dr. R. C. Dubey – Practical Microbiology